What is data integrity?
Data integrity is far more than just maintaining high-quality data. It's about establishing robust procedures that ensure the accuracy, reliability, and comprehensiveness of your data sources. It involves creating a transparent trail from each data point back to its original source, and seamlessly integrating data from diverse sources to provide convenient, holistic access.
Why data integrity is integral to achieving strategic finance
Although it can seem like somewhat of a “nice-to-have”, data integrity is a strategic imperative for FP&A.
At its core, data integrity ensures the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of financial data, which is vital for sound decision-making. Without it, strategic decisions risk being built on a foundation of flawed information, jeopardizing fiscal stability and organizational growth.
The importance of data integrity also encompasses compliance with regulations such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), which requires organizations operating in the European Union to establish clear, traceable, and secure data management practices. This forms a formidable line of defense against both external and internal threats which keeps your financial operations up and running.
Maintaining data integrity isn't just a small part of a successful FP&A strategy—it's the foundation of the entire Strategic Finance Pyramid. This foundation supports every layer, from budgeting and forecasting to strategic decision-making.
As with any structure, a weak foundation leads to instability. Therefore, without data integrity, every level of your strategy—budgeting, forecasting, and decision-making—becomes unstable. Accurate, reliable data means you can build strategies with confidence and focus on high-value activities instead of scrambling to correct errors or fill gaps.
Types of data integrity
Data integrity is crucial for finance leaders and FP&A professionals, and it's helpful to understand its two types: physical integrity and logical integrity.
Physical data integrity
Physical integrity pertains to the tangible security of the devices where your data is stored. Think of physical threats like power outages, natural disasters, or server failures. These can significantly disrupt your financial operations if precautions aren't in place. As a finance leader, ensuring your data infrastructure is robust and resilient is key to maintaining business continuity.
Local data integrity
Logical integrity, though more abstract, is equally vital. It concerns the accuracy, usefulness, and consistency of your financial data within a specific context. For instance, implementing blockchain technology in financial operations can bolster referential integrity by creating a secure and unalterable record of transactions. This ensures that changes to a primary key in one system do not lead to inconsistencies elsewhere.
There are four aspects of logical integrity:
- Entity integrity relates to each data point having a unique ID—akin to every transaction in your general ledger having a unique transaction number. This ensures data isn't duplicated and that no values are missing, which is crucial for accurate financial reporting and analysis.
- Referential integrity deals with the interplay between primary keys in one table and foreign keys in another, which is important for maintaining the integrity of hierarchical and relational databases. As an FP&A professional, you want to be sure that if a primary key gets deleted, it's not still referenced elsewhere, leading to erroneous analysis.
- Domain integrity guarantees that data is in a specified format. For example, if dates in financial reports should be in the YYYY-MM-DD format, any different format, like MM-DD-YYYY, would be flagged. This ensures consistency in data interpretation, vital for accurate financial forecasting and budgeting.
- User-defined integrity refers to custom rules that extend beyond entity, referential, or domain integrity. For instance, you might have a policy to include only active customers' data in a specific report. Such rules help tailor the data to your specific needs, making it more useful and relevant.
Many enterprise resource planning (ERP) and general ledger (GL) systems automatically handle this logical integrity. But as a financial leader, it's essential to make sure the data within these systems is clean, and any financial models built using this data reflect the same structural data integrity efforts. This ensures your financial insights, forecasts, and decisions are based on reliable, accurate, and relevant data.

Threats to data integrity
These days, there are quite a few risks to data integrity that businesses must develop responses to.
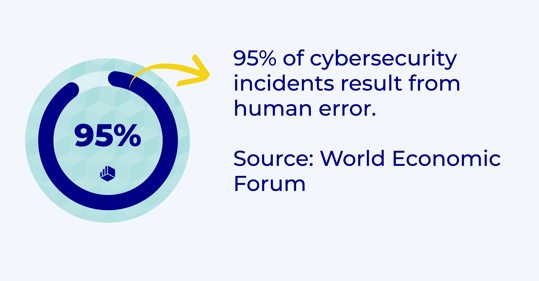
1. Human error
Let's start with the most obvious threat to data integrity: human error. When dealing with huge volumes of data, mistakes are inevitable—whether it’s a typo or even the accidental deletion of data. According to a 2023 Verizon Business study, human error is a factor in 74% of cybersecurity breaches, through phishing attacks, weak passwords, social engineering tactics, and more.
2. Technical malfunctions
Next, data integrity depends on hardware operating the way it's supposed to. What if a system experiences a malfunction or crashes? Without taking the proper precautions, you could lose mountains of data.
3. Data breaches
Data breaches and cyber-attacks are increasingly common dangers faced by companies of all sizes—not just the big guys like JP Morgan or Amazon. Attacks have increased across the board, with CrowdStrike’s 2024 Global Threat Report calculating a 75% increase in cloud intrusions. Data breaches not only threaten a company’s data integrity but also its reputation—especially when the company has been entrusted with sensitive customer data.
4. Poor integration
Data integrity largely revolves around consistent data handling procedures. This means standardizing data capture methods and formats so data from various sources can be properly integrated. Without proper integration, data can't be consistently analyzed and interpreted, which poses a huge problem for your FP&A strategy.
How to ensure data integrity for FP&A
As the foundation of accurate financial forecasts, actionable budgets, and data-driven decisions, you need to get as close to 100% perfect data integrity as possible. This calls for a systematic approach that eliminates inconsistencies, addresses vulnerabilities, and refers to an established FP&A framework. Here’s how to achieve that.
1. Assess your current data integrity status
Start by spring-cleaning your organization’s existing financial data. This involves:
- Conducting a gap analysis to identify discrepancies between current practices and best-in-class standards
- Reconciling data across different systems to pinpoint inconsistencies or redundancies
- Using root cause analysis to uncover the underlying issues whether they stem from human error, outdated processes, or siloed systems
AI validation systems can be particularly effective in identifying weaknesses in real time.
2. Prioritize each data integrity issue
Not all issues are equal—some pose a higher risk to financial accuracy than others. Assign priority levels based on their potential impact on strategic decision-making, compliance, or operational efficiency.
For example, an unresolved data breach might demand immediate attention, while inconsistent reporting formats may be a medium-priority concern. Categorizing these issues means you can allocate resources and effort more effectively and address critical vulnerabilities first.
3. Design and implement your solutions
Now you understand your priorities, you can develop targeted solutions for each issue. This may include:
- Automation tools to minimize manual errors. FP&A software is designed to automate repetitive tasks, such as data reconciliation, reducing the likelihood of human error in financial reporting.
- Standardized processes for data entry and reporting. Establishing a single chart of accounts across all departments makes sure you record financial data consistently and accurately throughout the organization.
- Security enhancements, such as multi-factor authentication or encryption, to protect sensitive information. Requiring multi-factor authentication for access to financial systems means that even if a hacker steals login details, they can’t access or even view critical data.
- Integration of systems to improve data flow across platforms. Connecting your ERP with budgeting tools synchronizes data in real time, eliminating silos and removing friction from your financial analysis.
Don’t forget to involve key stakeholders throughout the implementation process. This increases adoption and builds trust, which helps to maintain the integrity of your data over time.
4. Educate and train your finance team
Your data integrity plan will only be effective if everyone's on board. That’s why your team needs to understand your specific data governance policies, as well as the ALCOA principles, which make data attributable, legible, contemporaneous, original, and accurate. Try explaining some of the worst consequences of poor data protection and integrity (e.g., data breaches) to highlight how important it is to follow protocols.
Training should be ongoing. Everyone needs to stay up to date with changing policies and newer, more clever security threats. Hold a session covering these different and general data protection regulation and integrity practices at least once a quarter, if not more frequently.
5. Perform regular data integrity audits
Data management is not a one-and-done deal—it's an ongoing process that must be constantly re-evaluated. Are you still getting a lot of mileage out of your tools? Is your data governance policy still up to date?
To ensure data integrity, perform regular data quality audits. Establishing and tracking specific data quality KPIs helps identify and locate the source of any data integrity risks and problems. Some examples of data quality KPIs include:
- Data timeliness: the length of time it takes for users to access the data they need
- Data completeness: evaluates whether or not there are missing values in specific assets
- Data consistency: looks at how well different data sets work with each other
Utilize dashboards to display these metrics, making them easy to communicate to stakeholders. From there, you can devise and implement corrective actions to ensure data integrity.
Data integrity best practices
For a strong foundation of data integrity, you need a proactive approach to managing, securing, and validating your financial data. Luckily, there are proven practices that help you safeguard the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of your FP&A processes, and we’ve outlined them here.
Maintain data integrity with ALCOA
The ALCOA principles—Attributable, Legible, Contemporaneous, Original, and Accurate—offer a comprehensive framework for understanding and maintaining data integrity. They are equally crucial in the world of finance, where data drives strategy and decision-making.
Here’s a closer look at each principle:
Attributable
When it comes to maintaining financial data integrity, this principle is key for audit trails, access control, and accountability. Each recorded transaction in the general ledger must be traceable to the individual who made it, complete with the specific timestamp. This is a fundamental requirement for internal controls, auditing, and ensuring regulatory compliance.
Legible
Legibility of financial data ensures that any authorized team member can understand the recorded data without excessive effort. Financial reports and models should be easy to interpret and comprehend, with the goal of facilitating informed decision-making across the organization.
Contemporaneous
Contemporaneous recording of data, or capturing transactions “in the moment,” is a critical aspect of financial data integrity. It means that our financial models and reports are constantly updated to reflect real-time changes. This immediacy contributes to accurate financial forecasting, budgeting, and strategic planning.
Original
Originality demands that financial data should be the initial recording of the event or transaction. This principle supports the concept of a “single source of truth”—a central, unaltered database of records from which all other data is derived. It prevents confusion and discrepancies in data interpretation, which may result from multiple versions of data records.
Accuracy
In the context of financial data, accuracy not only implies the factual correctness of the data but also its appropriate form and context. Details should be drillable, providing a comprehensive, accurate view of financial data to allow for robust analysis and informed decision-making.
In essence, the ALCOA principles form the backbone of a strong data integrity strategy, crucial for maintaining trust in financial data and empowering accurate data and effective FP&A.
Prioritize data security
The terms data integrity and data security are often used interchangeably. While they're definitely not the same thing, you can't have integrity without security.
It’s worth noting that certain security practices* such as data encryption, mandating passwords, updating software, and developing a data breach response plan are jobs for the office of the CTO. However, it’s helpful to understand how these practices coincide with other security precautions.
Maintaining data security may involve:
- Setting up access levels: Employees should only have access to data that they need. Limiting entry points greatly reduces the risk of data breaches and strengthens data security.
- Encrypting data*: What if data is intercepted by bad actors? Encryption ensures it can't be read.
- Mandating strong passwords and 2FA*: Ensure employees use strong passwords with upper-case letters, numbers, and special characters on work and personal devices. Also, make sure devices use 2FA, a system that requires a password in addition to confirmation from a second device. This adds another safety barrier, preventing access to hackers even if they have your login details.
- Vetting third parties: These days, we all work with third parties. They can make our work lives a lot easier and help improve our bottom line. That being said, it's crucial to evaluate their security measures before working with them to prevent data breaches or leaks that could damage your company's reputation and lead to potential legal consequences.
- Backing up data: Backing up data is a standard data security practice that guards against both physical threats and malfunctions. Backups should be kept off-premises.
- Updating software*: Regular system and software updates help prevent bad actors from utilizing "backdoor" exploits.
- Being proactive*: As part of its data security measures, your company should utilize penetration testing and vulnerability scanning, and develop a data breach response plan. In a worst-case scenario where customer data does become compromised, plan a transparent response.
- Establishing clear-cut reporting procedures: As mentioned earlier, you should educate employees on data security and different types of threats. You also need to have clear-cut reporting procedures in place so that, once identified, threats can be quickly escalated.
Leveraging technology to validate data
Data validation assesses the quality, structure, and relevance of data before it's used by your business. As such, it's a critical data integrity process, right up there with security practices.
Look for software that includes built-in validation features, rather than having to manually scrounge through huge volumes of data. When software has built-in validation features, it means the software will look at data as soon as it's entered. If there are any inconsistencies or anomalies, it will alert you and refrain from adding the data to the database.
Technology also helps address another threat to data integrity: human error. That's because most software with built-in validation also leverages automation. With automation, data is recorded as it appears in a standardized, consistent manner.
Standardize data collection and entry processes
We've mentioned consistency a few times—why's it so important? Consistency ensures each piece of data can be easily compared to every other piece. This makes it much simpler to identify trends or anomalies and streamlines the data validation process.
To guarantee consistency, you'll need to standardize data collection and entry processes. When all data is recorded in the same format, it makes it much easier to integrate into an existing relational database without modifying it.
Additionally, maintaining data consistency makes the process of implementing FP&A solutions much smoother down the road. When there is a standardized chart of accounts and other metadata used across the organization, mapping those types of hierarchies provides quicker time to value and easier apples-to-apples comparisons of your data.
Understand data dictionary and metadata
Metadata is foundational in fostering and preserving data integrity in FP&A reporting. It functions as the backbone that describes, explains, and locates data, thereby providing a clear and accessible framework that enables accurate and reliable reporting.
To begin with, metadata adds a layer of transparency to FP&A reporting by detailing the origin, time, structure, and nature of data assets. This transparency becomes critical when tracing back data points to their original sources for verification, auditing, or compliance purposes.
In FP&A, where decisions are made based on financial forecasts, trends, and other statistical information, it is crucial to ensure that the data being utilized is accurate, timely, and reliable. Metadata, by providing contextual and comprehensive information about the data assets, supports this requirement, helping to maintain data integrity.
The data dictionary, which serves as the central repository for metadata, significantly contributes to data mapping and integration. Often in FP&A, data comes from various sources, both internal and external, that can have different formats and structures. The process of aligning these disparate data assets can be complex and challenging.
However, with a data dictionary, this integration becomes much more streamlined and manageable. By presenting the relationships between data assets across sources, the data dictionary helps to prevent inconsistencies and errors that could arise during data integration. This, in turn, leads to higher data integrity and enhances the credibility of FP&A reports.
Don’t overlook data integrity in FP&A
Fostering data integrity in FP&A reporting isn't just a best practice; it's an essential part of strategic decision-making, regulatory compliance, and building trust within your organization and with stakeholders. Keeping these tips in mind is a great first step toward safeguarding the accuracy, consistency, and reliability of your financial data.
Want to learn how Cube can help you foster data integrity in your FP&A reporting with ease? Request a free demo today.


.png)



.png)